Comparing Li-ion vs LFP vs Flow Batteries: Pros & Cons
Choosing the right battery for energy storage is critical as renewable energy adoption grows. Homeowners, businesses, and industrial users often face the decision between Li-ion, LFP, and Flow Batteries. Each technology has unique advantages and disadvantages. In this guide, we’ll explore the pros and cons of Li-ion vs LFP vs Flow Batteries, helping you select the best energy storage solution for your needs.
1. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Batteries
Overview:
Li-ion batteries are widely used in electric vehicles, home energy systems, and portable electronics due to their high energy density and efficiency.
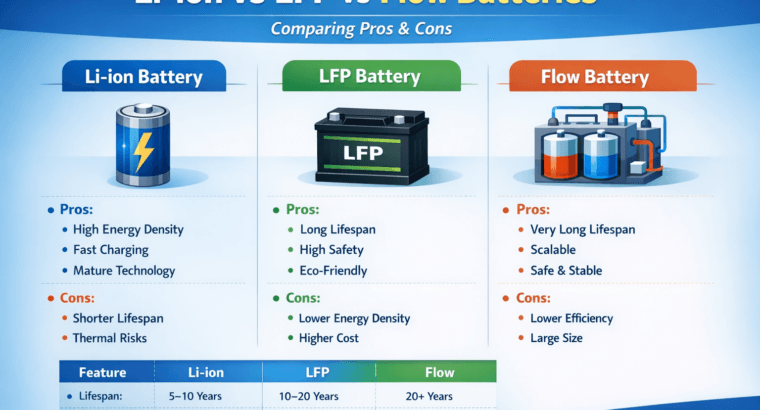
Pros:
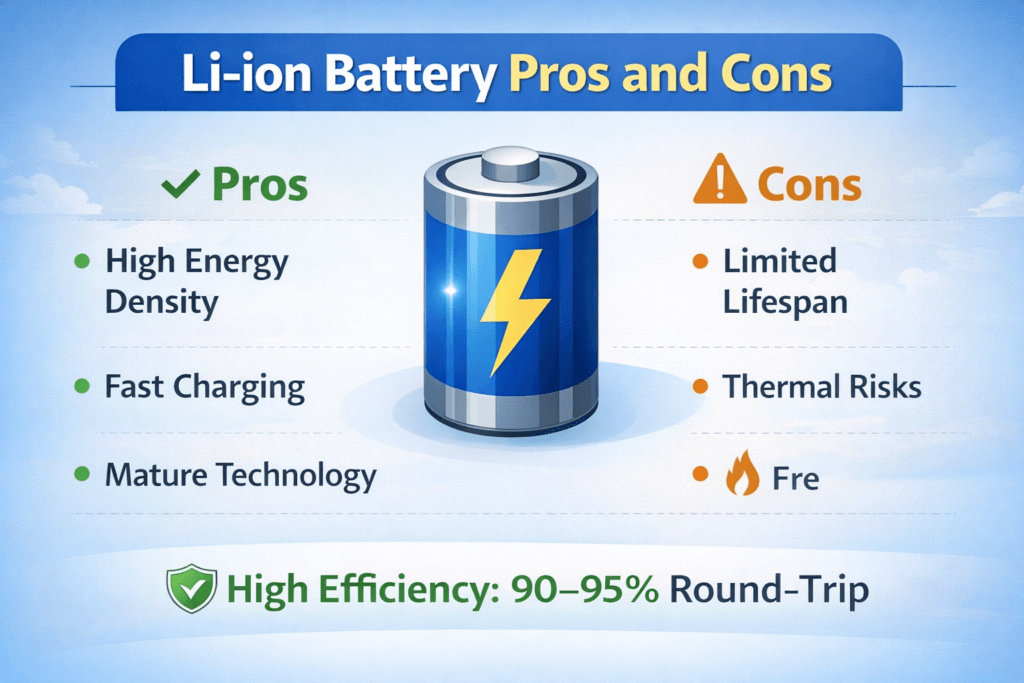
- High energy density: stores more energy in a compact space.
- High efficiency: 90–95% round-trip efficiency.
- Fast charging and discharging.
- Mature, widely available technology.
Cons:
- Limited lifespan: typically 5–10 years.
- Thermal risks: can overheat or catch fire if damaged.
- Higher upfront cost than some alternatives.
Best Use Cases:
- Residential energy storage
- Electric vehicles
- Backup power systems
Explore Li-ion batteries on F2CDeals
2. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Batteries
Overview:
LFP batteries are a type of lithium battery using iron phosphate as the cathode, offering improved safety and longer lifespan.
Pros:
- Long lifespan: 10–20 years.
- High thermal stability: safer than traditional Li-ion.
- Eco-friendly and sustainable.
- Maintains performance at high temperatures.
Cons:
- Lower energy density: larger for same capacity.
- Higher upfront cost, but cost-effective over time.

Best Use Cases:
- Residential and commercial solar energy storage
- Industrial backup systems
- Long-term energy storage solutions
Explore LFP batteries on F2CDeals
3. Flow Batteries
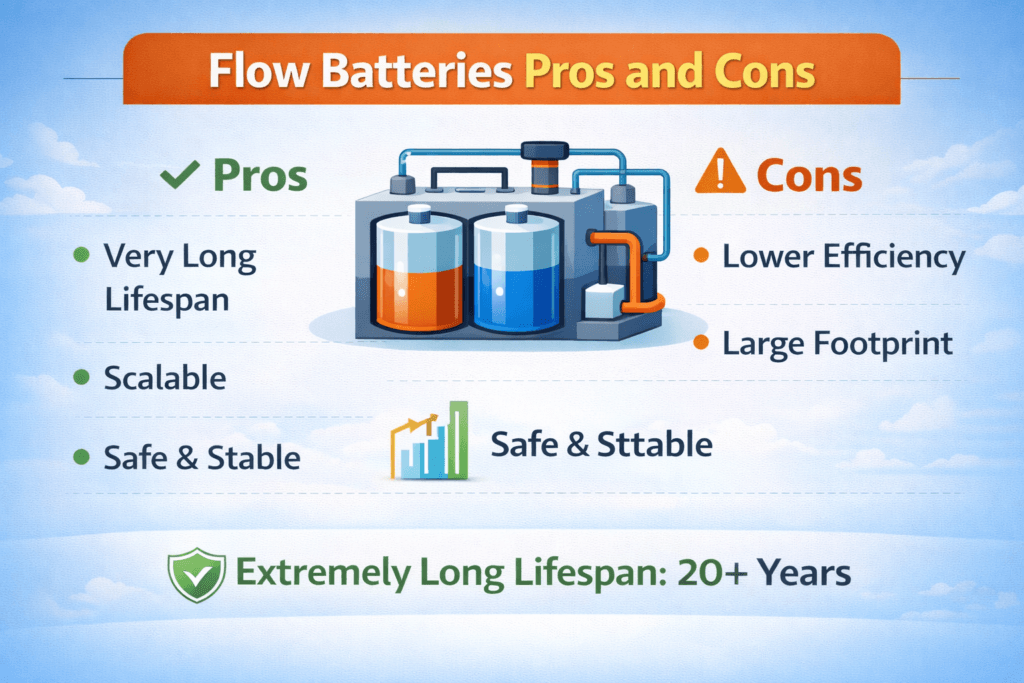
Pros:
- Extremely long lifespan: 20+ years.
- Scalable: easy to increase capacity.
- Safe and stable: non-flammable.
- Can discharge deeply without damage.
Cons:
- Lower efficiency: 65–85% round-trip.
- Large footprint: requires more space.
- Complex installation and maintenance.
Best Use Cases:
- Utility-scale renewable energy storage
- Microgrids and remote energy systems
- Industrial facilities with high energy demands
Explore Flow batteries on F2CDeals
Comparison Table: Li-ion vs LFP vs Flow Batteries

| Feature | Li-ion | LFP | Flow Batteries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High | Medium | Low |
| Lifespan | 5–10 years | 10–20 years | 20+ years |
| Efficiency | 90–95% | 90–95% | 65–85% |
| Safety | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Cost (Upfront) | High | Medium-High | High |
| Scalability | Moderate | Moderate | Excellent |
| Best Use Cases | EV, Home storage | Solar, Commercial | Grid, Industrial |
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the main difference between Li-ion, LFP, and Flow batteries?
The main difference lies in chemistry, lifespan, safety, and scalability.
Li-ion batteries offer high energy density and compact size, LFP batteries provide better safety and longer lifespan, while Flow batteries excel in large-scale, long-duration energy storage with extremely long life cycles.
Which battery type is safest for home energy storage?
LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries are considered the safest for home energy storage due to their high thermal stability, low fire risk, and resistance to overheating compared to traditional Li-ion batteries.
Are Li-ion batteries still a good choice in 2026?
Yes, Li-ion batteries are still widely used in EVs, portable electronics, and compact energy storage systems. However, for stationary storage, many users now prefer LFP batteries due to longer lifespan and better safety.
Why are Flow batteries not commonly used in homes?
Flow batteries require large tanks and complex systems, making them less suitable for residential use. They are mainly used in industrial, utility-scale, and grid-level energy storage projects where space is not a limitation.
Which battery has the longest lifespan?
Flow batteries have the longest lifespan, often exceeding 20–30 years with minimal degradation. LFP batteries typically last 10–20 years, while standard Li-ion batteries last 8–12 years depending on usage.
What is the most cost-effective battery for solar energy storage?
For most homeowners, LFP batteries offer the best long-term value due to their long cycle life, safety, and low maintenance. While Flow batteries have a high upfront cost, they become cost-effective for large-scale, long-duration storage.
Can LFP batteries be used for off-grid solar systems?
Yes, LFP batteries are ideal for off-grid and hybrid solar systems because they support deep discharge cycles, long lifespan, and stable performance in varying temperatures.
Which battery technology is best for future energy storage?
There is no single best solution.
- Li-ion: Best for compact, high-power applications
- LFP: Best for residential and commercial energy storage
- Flow batteries: Best for grid-scale and long-duration energy storage
Future energy systems will likely use a mix of all three technologies.
Conclusion
When comparing Li-ion vs LFP vs Flow Batteries:
- Li-ion: Compact, high-efficiency applications.
- LFP: Safe, long-lasting, and reliable.
- Flow Batteries: Perfect for large-scale, industrial, or utility storage.
Leave your comment